Ease of importing goods score: B
Ease of doing business 3/5
- South Korean ecommerce consumers are sophisticated and globally-aware buyers. They are enthusiastic, loyal, and tech-savvy shoppers.
- South Korea has less clear-cut regulations and are more hesitant toward foreign business models.
- South Korea also has very competitive domestic prices.
Landed cost fairness 4/5
- South Korea’s de minimis, import tax, and average duty rates are fair, which is favorable for landed cost.
- There are many free trade agreements (FTAs) in place (especially with big markets), which allows for easier trade.
Flexibility of legal regulations 3/5
- South Korea maintains an import declaration system that allows for the release of goods without delay upon acceptance of an import declaration certificate without error.
- South Korea’s government has established requirements and procedures for importing certain products including registration, standards, and safety. There’s also efficacy testing to ensure the protection of public health and sanitation and more.
Availability and accessibility of shipping 5/5
- South Korea has many carrier options and services in the high-traffic Asian trade route between Japan and China.
Accessibility and variety of payment methods 5/5
- South Korea accepts a variety of popular payment methods, but their preferred methods are credit cards and variations of smart pay.
Market opportunity 5/5
- South Korea has one of the top 10 largest ecommerce markets in the world.
- South Korea’s ecommerce market growth steadily increases.
- Nearly 100% of South Korea’s population uses the internet, giving sellers the potential for high ecommerce success.
Key stats for South Korea
| Population | 51.44 million (2022) |
| GDP | 1.81 trillion USD (2022) |
| GDP per capita | 42,500 USD (2020) |
| Internet penetration | 98% of the population use the internet (2022) |
| Ecommerce users | 68% of the population shop online (2022) |
| Leading product categories | Food and beverages; home appliances and electronics; food service; clothing; household items; cosmetics; and travel/transportation services |
| Preferred online payment method(s) | Credit card, mobile payments, and digital wallets (smart pay) |
| Languages | Korean |
| Currency | South Korean won/KRW/₩ |
Landed cost for South Korea
The landed cost for a cross-border transaction includes all duties, taxes, and fees associated with the purchase. This includes:
- Product price
- Shipping
- Duties
- Taxes
- Fees (currency conversion, carrier, broker, customs, or government fees)
South Korean de minimis, tax, and duty
Further explanation of duty, tax, and de minimis is provided below
Duty and tax de minimis
- Duty and tax de minimis: 150 USD
- Duty and tax de minimis for U.S. and/or Puerto Rico-origin shipments: 200 USD
Based on the FOB value of the order
De minimis value
Duty and tax will be charged only on imports into South Korea where the total FOB value of the import exceeds South Korea’s minimum value threshold (de minimis), which is 150 USD. Anything under the tax de minimis value will be considered a tax-free import, and anything under the duty de minimis value will be considered a duty-free import. U.S.-origin shipments valued under 200 USD will be considered tax-free and duty-free imports.
Import tax
- Standard tax: 10%
- Special excise tax rate: 10-20%
Applied to the CIF value of the order
Value-added tax (VAT)
VAT is charged on the CIF value of the order. This VAT is charged at the general rate of 10%, but in specific cases, there is an excise tax rate charged between 10% and 20%. These specific cases include certain luxury items and durable consumer goods (i.e. automobiles).
Import duty
- Average rate: 8%
Applied to the CIF value of the order
Average import rate
Like VAT, duty is charged on the CIF value of the order, which means that duty is calculated based on the price of the goods, plus the cost of packing, freight, and insurance. The average duty rate is 8%.
Landed cost examples for South Korea
Below are sample landed cost breakdowns for South Korea calculated using Zonos Quoter:
Landed cost for a shipment to South Korea below the de minimis value:

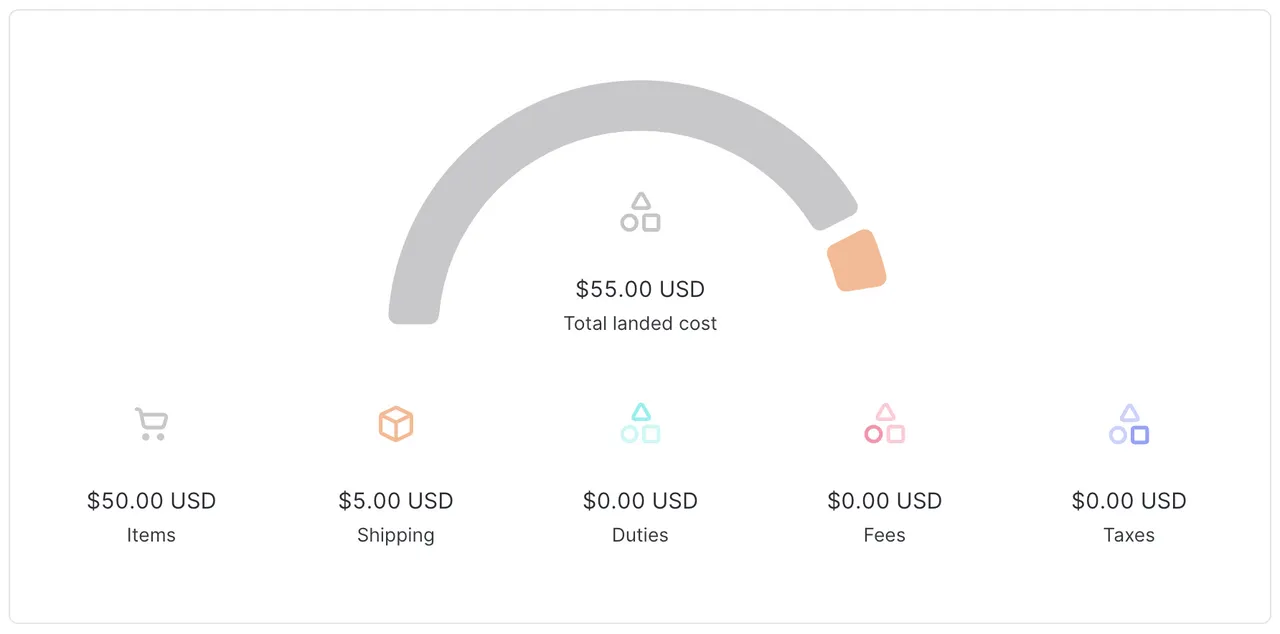
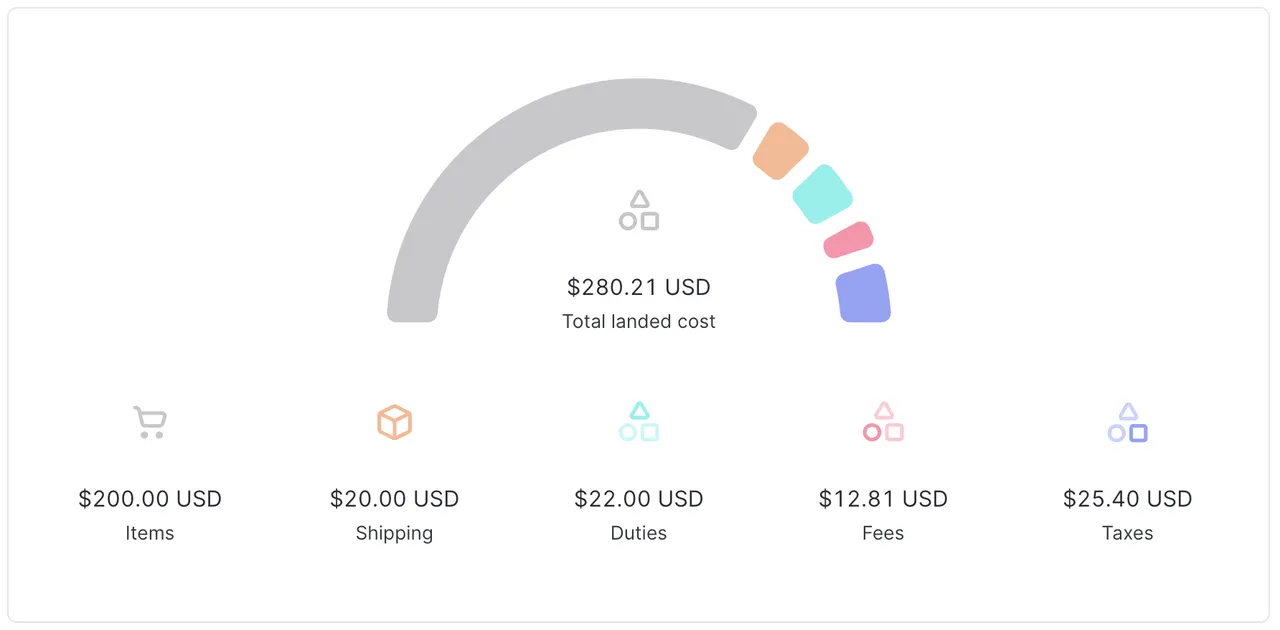
Landed cost for shipment to South Korea above the duty and tax de minimis values:


Trade agreements
South Korea has at least 17 trade agreements, which include 57 countries. These trade agreements offer a zero or highly discounted duty rate for goods made in a participating country.
South Korea is a member of the World Trade Organization
As a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO), South Korea must abide by the most-favored-nation (MFN) clause, which requires a country to provide any concessions, privileges, or immunities granted to one nation in a trade agreement to all other WTO member countries. For example, if a country reduces duties by 10% for one country, the MFN clause states that all WTO members will have their duties cut by 10% into that country.
Customs resources
South Korea’s Customs authority
Customs refund in South Korea
Note: Talk to your carrier about customs refunds.
Shipping and compliance
Top courier services:
- Korea Post
- DHL Express
- FedEx
- UPS
- CJ Logistics
- Lotte Global Logistics
Depending on the courier, additional shipping fees may include the following:
- Tracking fee
- Insurance fee
- Fuel surcharge
- Remote delivery charge
- Signature fee
- Overweight or oversized fee
- Special handling fee
- Dangerous goods fee
Documentation and paperwork
- Bill of lading or air waybill
- Commercial invoice
- Packing lists (two copies required)
- Maritime insurance
- Import declaration
- Special documentation (for food, agriculture, etc.)
Restricted, prohibited, and controlled items
Government agencies regulate imports.
Prohibited items:
- Pornographic materials
- Subversive material
- Treasonous material
- Books, photos, and film that violate constitutional orders, or might be harmful to public peace and customs
- Items that contain confidential information on government or intelligence activities
- Counterfeit money, banknotes, bonds, and other securities
Restricted items:
- All weapons
- Illegal drugs (opium, marijuana/cannabis, cocaine, etc.)
- Precious metals
- Cultural properties
- Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) hormone drug
- Soil
- Jerky, hams, and sausage products
- Importation of synthetic nicotine for electronic cigarettes
- Goods subject to the laws on the treatment and movement of waste matter between countries
- Plants, fruits, vegetables, and agricultural products
- Animal products, livestock, and animal fodder
- And more
Legal regulations for businesses
Enforcement Decree of the Licensed Customs Broker Act
In January 2022, South Korea implemented the Enforcement Decree of the Licensed Customs Broker Act. The Licensed Customs Broker Act was intended to create an institution for licensed customs brokers to secure the convenience of duty payers and the efficiency of the customs clearance process, which in turn, contributes to the growth of the national economy. This decree has been put in place to provide Licensed Customs Brokers with the necessary materials and abilities to enforce the original law.
Tips for exporting from South Korea
There are rules and procedures that South Korean exporters need to be aware of prior to exportation.
What is the main driver of ecommerce market growth in South Korea?
The high penetration of smartphones is currently the most consequential element causing ecommerce market growth in South Korea. Purchases made on mobile phones increased from 74.8 billion USD (2019) to 92.1 billion USD (2021).
South Korea country guide
Learn about cross-border ecommerce, shipping, and importing.
If you are looking to grow your ecommerce business into South Korea , you’ve come to the right place. Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about selling goods into South Korea.
, you’ve come to the right place. Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about selling goods into South Korea.