Ease of importing goods score: B
Ease of doing business 5/5
- Germany has a mature ecommerce market and savvy online shoppers.
- Germany is the fifth largest ecommerce market in the world.
Landed cost fairness 1/5
- The duty and VAT rates are high, which is unfavorable for landed cost.
- Germany’s de minimis is fairly low, which is also not favorable for landed cost.
Flexibility of legal regulations 5/5
- Germany’s customs regulations fall under the European Union’s (EU), which are reasonable and allow for easier trade.
Availability and accessibility of shipping 5/5
- All major couriers ship to Germany.
Accessibility and variety of payment methods 5/5
- Germany accepts a variety of popular payment options, such as PayPal, ewallets, invoice, credit card, Paydirekt, direct debit, etc.
Market opportunity 5/5
- The majority of Germany’s population shop online, giving sellers the potential for high ecommerce success.
- Germany’s market is favorable to expand into because it has the fifth largest ecommerce market in the world.
Key stats for Germany
| Population | 84.3 million (2022) |
| GDP | 4.03 trillion USD (2022) |
| GDP per capita | 48,810 USD (2022) |
| Internet penetration | 93% of the population use the internet (2022) |
| Ecommerce users | 82% people in Germany shop online (2022) |
| Leading product categories | Fashion, media (books, music, movies, and video games), and electronics (computers) |
| Preferred online payment method(s) | Ewallets, PayPal, invoice, credit card (Visa and Mastercard), Paydirekt, and direct debit (Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA)) |
| Languages | German and English |
| Currency | Euro/EUR/€ |
Landed cost for Germany
The landed cost for a cross-border transaction includes all duties, taxes, and fees associated with the purchase. This includes:
- Product price
- Shipping
- Duties
- Taxes
- Fees (currency conversion, carrier, broker, customs, or government fees)
German de minimis, tax, and duty
Further explanation of duty, tax, and de minimis is provided below
Duty and tax de minimis
- Tax de minimis: 0 EUR
- Duty de minimis: 150 EUR
Based on the FOB value of the order
De minimis value
Duty and tax will be charged only on imports into Germany where the total FOB value of the import exceeds Germany’s minimum value threshold (de minimis), which is a duty de minimis of 150 EUR and a tax de minimis of 0 EUR. Anything under the duty de minimis value will be a duty-free import, but because the tax de minimis is zero, every import is subject to tax.
Value-added tax (VAT)
- Average VAT rate: 19%
- Reduced rate: 7%
Applied to the CIF value of the order
VAT - Value-added tax
Import VAT is charged on the CIF value of the order. VAT is charged at the standard rate of 19%, but certain products, such as food, books, hotel accommodations, cultural services, and more, receive a reduced rate of 7%. The EU employs IOSS (Import-One-Stop-Shop) as their method for collecting VAT.
Average duty rate
- Average duty rate: 4.2%
Applied to the CIF value of the order
Import duty
Like VAT, duty is charged on the CIF value of the order. The duty ranges from 0-17%, with an average rate of 4.2%.
Landed cost examples
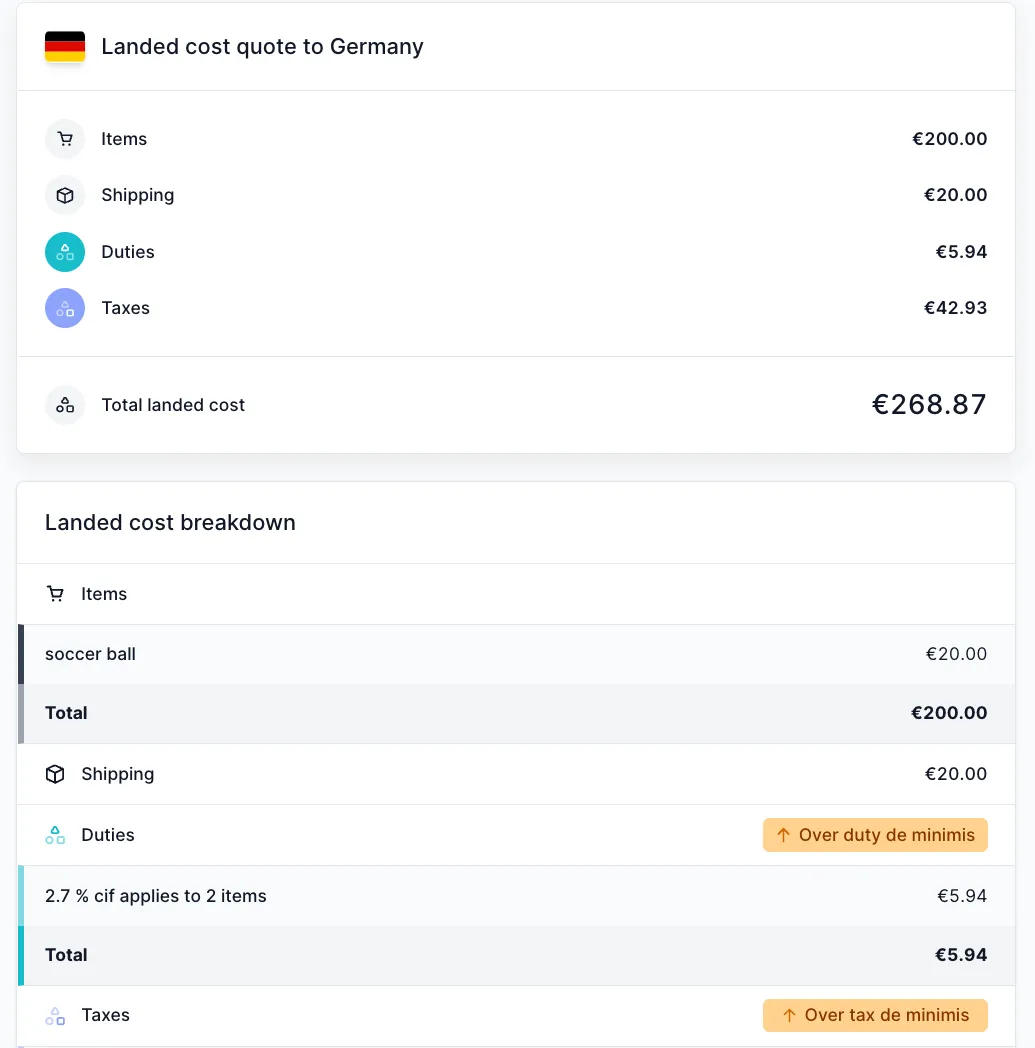
Below are sample landed cost breakdowns for Germany (one below and one above the duty de minimis threshold) calculated using Zonos Quoter. Since the tax de minimis is 0 EUR, tax will always apply:
Landed cost for a shipment to Germany below the duty de minimis value:


Landed cost for shipment to Germany above the duty and tax de minimis values:

Trade agreements
Germany, being a member of the EU, has at least 60 trade agreements. These trade agreements offer a zero or highly discounted duty rate for goods made in a participating country.
Germany participates in the European Union's Common Customs Tariff, which applies preferential rates to imports from other countries with which the EU has signed agreements.
Germany is a member of the World Trade Organization
Germany is a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO). Therefore, Germany must abide by the most-favored-nation (MFN) clause, which requires a country to provide any concessions, privileges, or immunities granted to one nation in a trade agreement to all other WTO member countries. For example, if a country reduces duties by 10% for one country, the MFN clause states that all WTO members will have their duties cut by 10% into that country.
Customs resources
Germany’s Customs authority
European Commissions - Customs
Customs refund in Germany
Note: Talk to your carrier about customs refunds.
Shipping and compliance
Top courier services:
- DHL Express (Deutsche Post DHL)
- FedEx
- UPS
- USPS
- Hermes
- DPD
- GLS
Depending on the courier, additional shipping fees may include:
- Tracking
- Insurance
- Fuel surcharge
- Remote delivery charge
- Signature fee
- Overweight or oversized fee
- Special handling fee
- Dangerous goods fee
- etc.
Documentation and paperwork
Always required:
Sometimes required:
-
Economic Operators Registration Identification (EORI)
-
Tax ID number
-
Germany Power of Attorney (POA) form needed for clearance
Restricted, prohibited, and controlled items
Government agencies regulate imports.
Prohibited items:
- All products containing the biocide dimethyl fumarate (DMF)
- Certain carcinogenic substances
- Certain chemicals subject to the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC)
- Certain pesticides subject to the Rotterdam Convention
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
- Counterfeit coins
- Counterfeit or pirated goods
- Fighting dogs
- Flick and gravity knives
- Fully Automatic weapons
- Live animals
- And more
Restricted items:
- Animal carcasses or products
- Animal feed
- Animal pathogens and rabies virus
- Animals, birds, and other Livestock
- Antiques
- Coffee samples
- Computer software
- Drugs, prescription and non-prescription
- Explosives – 1.3 and 1.4S excluding UN0349, UN0384, UN0481
- Fabrics and fabric samples
- Furs
- Hair and wool
- Hay and straw
- Medical samples
- Medical/dental supplies and equipment
- Non-perishable foods (except candy and chocolates)
- Plants
- Tapes, computer
- Textile articles (require a certificate of origin)
- Tobacco
- Unprocessed wood
- Used agricultural machinery
- Video senders, equipment capable of transmitting video images
- And more
Legal regulations for businesses
Classification
The Combined Nomenclature (CN) is used to classify most goods when they are declared to customs in the EU. The CN document is updated and published every year, and the latest version can be found on the European Commission's website.
Customs declarations
The Single Administrative Document (SAD) and Summary declaration are documents used for customs declarations.
Identification number
Economic Operators Registration and Identification number (EORI) is an identification number for the importer. Generally, a business needs to provide an EORI (for business-to-business shipments), but a business-to-consumer shipment does not need an EORI upon import.
Rules and VAT rates
Each country in the EU applies the standard VAT rules differently, and each country has different VAT rates.
Tips for exporting from Germany
There are rules and procedures that EU exporters need to be aware of prior to exportation.
How do I comply with the EU VAT scheme?
There are several different shipping options to choose from in order to remain compliant with the EU’s VAT scheme. Zonos' EU VAT guide has further information about your options.
What does ICS2 require retailers to do?
Everyone who ships to Europe and the UK is impacted, e.g., online retailers, manufacturers, and exporters, must ensure they have accurate information regarding the recipient and package contents before they send the shipment through the carrier or postal operator to the EU or the UK.
Germany country guide
Learn about cross-border ecommerce, shipping, and importing.
If you are looking to grow your ecommerce business into Germany , you’ve come to the right place. Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about selling goods into Germany.
, you’ve come to the right place. Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about selling goods into Germany.